In this step-by-step guide, I’m going to explain exactly how to create an effective SEO strategy and how to implement it.
This is the exact SEO approach that I followed to grow search traffic to over 1.5 million for one of my sites. And, as you can see in the image below, 86% of traffic is organic (search).
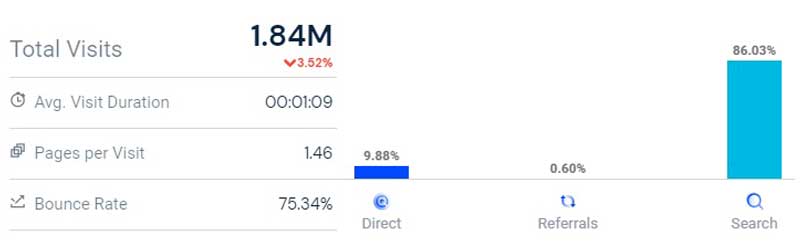
So if you also want to increase your organic traffic then this post is for you.
I – SEO Strategy: Understanding the Basics
But what the heck is SEO strategy?
1) What Is SEO Strategy?
SEO Strategy DEFINITION: SEO strategy is a detailed plan designed to improve search engine rankings and drive more organic traffic.
In other words: SEO strategy is a step-by-step process that you plan and implement when you want to get more organic traffic to your website.
SEO strategy is also called SEO approach and more than often inter-changed with SEO tactic. But strategy and tactic are not the same things.
That is the classic definition of SEO strategy.
To be more pragmatic: SEO marketing strategy is all about being where the audience is. It’s about delivering relevance and value to your target audience.
It’s also about managing your brand reputation online — guiding searchers (with relevant content) along the customer journey.
As you become a trusted brand, people will give you preference over your competitors when it comes to making a purchase.
2) Why Do You Need an SEO Strategy?
Your SEO strategy matters…
75% of searchers don’t scroll past the first page on Google search results? (SEO Statistics)
SEO brings in 20X more clicks and 150% higher ROI compared to paid advertising. – Sparktoro
75% SEO acquires customers at 75% lower CAC than any other paid channel. – Terakeet
5X-Companies receive 5X more value from Google Search than Google Ads. – Google
These marketing statistics prove that SEO still works. And therefore, you need an effective SEO strategy.
3) The Problem with SEO Strategy Templates & Checklists
Many marketers follow some sort of SEO strategy template suggested by the gurus. Which I think is a wrong approach.
Each business is different in terms of products, objectives, geo-location, audience, budget, etc.
There is no fit-for-all SEO strategy template that can be followed blindly.
Therefore, rather than following a ready-made SEO strategy template, you should design an SEO strategy that meets your specific goals.
4) SEO Strategy vs. SEO tactics
The terms strategy and tactics are frequently confused.
Marketers often use these terms interchangeably, while these two are different concepts.
This is one of the reasons why most SEO strategies fail.
Strategy without tactics is the slowest route to victory. Tactics without strategy is the noise before defeat. – Sun Tzu
An SEO strategy is an overall process you use to increase organic traffic to your website. It includes the planning stage, detailing, and implementing steps. A solid SEO strategy aids in the identification of the broader picture.
On the other hand, SEO tactics refer to the particular actionable steps you take to realize your search engine optimization (SEO) strategy goals.
For example, an SEO strategy goal could be to rank high on SERP and generate more search traffic.
An SEO tactic could be to create more SEO content or link building – that will aid to achieve your SEO strategy goal, to drive more organic traffic.
Likewise, an SEO tactic can be to create more SEO content or earn more backlinks. This will help you achieve your SEO strategy goal which in this case is to bring in more organic traffic.
II – SEO Strategy: Benchmarking & Goals Setting
1) Benchmarking the Current SEO Performance
It’s practically impossible to have a plan to take your site to the next level if you don’t know how it’s functioning right now.
As a result, measuring your present performance should be the first step in developing your strategy. It would be best if you were benchmarking performance across the following areas as a starting point:
• Visibility (Organic traffic)
• No. of keywords rankings and their positions
• Branded and non-branded traffic split
• Top pages by traffic
• Backlinks acquired
• Etc.
You can use an SEO tool to collect the information you’ll need to develop your approach.
For example, I’m using the SEMrush Organic Research Tool. Once you log in to the tool, on the ‘Traffic’ page of the overview dashboard, the ‘Estimated Traffic Trend’ displays your current (and past) organic visibility.
On the same page, you can examine the breakdown of branded and non-branded traffic. Finally, the predicted traffic trend shows you details about your site’s exposure changes over time and how well it is currently performing.
Given that now the bulk of branded searches are conducted by those already aware of your business, knowing how your branded and non-branded traffic split helps you uncover opportunities.
Non-branded traffic growth usually coincides with the addition of new users who may have never heard of you before. On the ‘Positions’ page of the tool, you can see a breakdown of your site’s current ranking positions as well as the evolution of indexed keywords usage over time.
You can develop a comprehensive picture of how your site is performing right now by starting to collect these insights before creating goals and putting in place a plan to help you move from your current stand to where you wish to be in the future.
Then, to completely picture your recent performance, combine the insights acquired from the Organic Research tool with business-related data from Google Analytics or your platforms about revenue, conversion rates, and leads created, etc.
You can use any other SEO tool you prefer such as Ahrefs and Similarweb etc.
2) Setting the KPIs and SEO Goals
Define Your SEO goals. Setting objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) is likely the most crucial aspect of developing an SEO plan.
You must be aware of where you wish to go to create an action plan for getting there, assess your success, and know when you’ve met your objectives.
But first, let’s define the distinction between goals and KPIs, as you’ll need each.
• Goals are what you desire to attain in the end.
• KPIs are metrics that show how far you’ve come toward your objectives.
When it comes to SEO, both terms are frequently interchanged, but you must define both throughout the plan design step.
From the definition given above, we know that the primary goal of your SEO strategy is to drive more search traffic to your website.
However, the goal for “attracting search traffic” is a vague one. Therefore, your SEO goals should be clear, tangible, and measurable.
Some of the probable SEO goals could be traffic quantity, conversion, sales, ROI and revenue, etc.
If traffic is your goal, how much and when?
If the conversion is your goal, what is the right ROI for your business? Is it through lead generation or demand generation?
If the sales are your goal, for which product, how much?
So, you need to set your goals before you design your SEO strategy.
III – 7 Steps to Create an Effective SEO Strategy
Then, how to create a profitable SEO strategy for 2023?
Before we discuss the steps needed to create an organic search strategy, it’s important to understand the certain key factors that we need to consider while designing an SEO strategy.
SEO strategy is designed based on several factors including your SEO goals, budget, content strategy, on-page SEO, off-page SEO and link building, technical SEO, content amplification & promotion, and user experience, etc.
All this boils down to content creation, optimization, link building, and content marketing.
Below you’ll find a tried-and-tested process to help you develop a winning SEO strategy.
Step #1: Keyword Research
Keyword research is a must. This is the foundation of any legit SEO strategy. Without target keyword phrases, you cannot create an effective search traffic strategy.
For higher Google rankings, you need to target specific search terms through content creation and promotion.
How to find target keywords?
Google Suggest
Google Suggest is my favorite keyword research tool.
Terms suggested by Google make great keywords for search traffic as they come straight from the big Daddy.
Prepare a list of those keywords and use any of the keyword tools (SEMrush, Ubersuggest, etc.) to check out the search volume and competition levels for those terms.
Once you have a list of keywords, you’re ready for the next step.
Step #2: Competitive Analysis
Analyze the SEO strategies of your competitors.
SEO competitive analysis is about analyzing your competitors’ online presence, especially the search engine rankings.
You need to evaluate your competitors’ for the following:
• Organic search rankings
• Content strategy
• Backlink profile
• Social media strategy/online reputation
• Site design and user experience (UX)
• Etc.
Method #1: Analyze Google’s First Page
This is the most effective way to perform competitive analysis.
Once you prepared a list of the most relevant keywords, it’s time to find who is ranking for your most important keywords.
For that, check out Google’s page one (and page 2, if you want more data).
It will give you an idea of what is already ranking.
These are your online (SEO) competitors.
Look at the search result pattern. See what Google (or Bing) is showing on the first page.
What kind of pages are there on the top – content type, images, maps, videos, etc.
List down the top 10 or 20 search results.
Then, visit these pages/sites and check for the following:
a) Content Types: For example, is it a list post or a step-by-step guide? Does it include tons of visuals – images, Infographics, etc.? OR is it a video tutorial? So on…
b) Authority: Check for the page’s/site’s backlink profile. What kind of backlinks does the site have, and from where, how many, etc. What are their Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA)?
c) Online Reputation: How many social shares/likes the pages have earned.
All these factors are important to rank high on SERP.
You may want to use SEO tools to perform competitive research. Tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, etc. will make your job a lot easier and effective.
Let us understand the whole process with the above example:
In the example, I did keyword research for a home & garden topic. And, prepared a list of the most relevant keywords.
Here, I’ll perform a competitive analysis using Google search.
First, I’ll find the most popular sites in the niche. I searched for the term “best trees for backyard” on Google and here’s what I found:
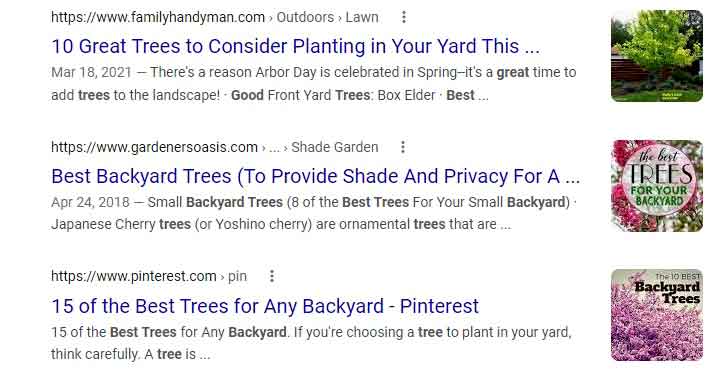
From the top 10 results, I found (as you can see in the image above) the following:
a) Content Types:
1. All of the top results are list posts
2. All pages have a lot of high-definition images.
b) Backlink Profile and Authority:
Next, find the backlinks of the pages that appeared in the top results.
I utilize a nifty tool Ubersuggest to find backlinks of the pages. For instance, here are some of the backlinks the (bhg.com) page has acquired over time:
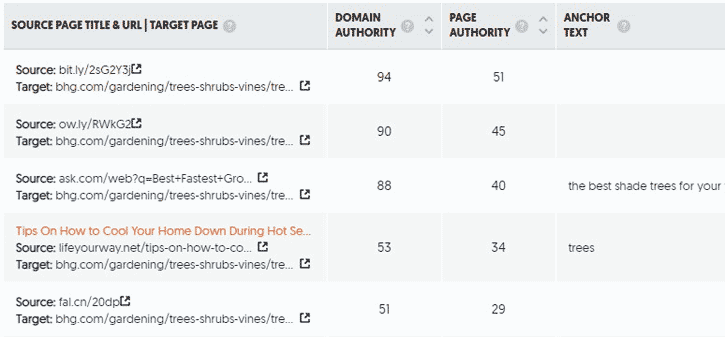
Prepare a list of all the backlinks these pages have. (We will need this list later, during the off-page SEO process).
Next, I’ll check for the authority of the top-ranking competitors:
DA and PA: From the SERP above, I found that Domain Authority (DA) of the top 10 results varied widely – from DA 20 (dogwoodlandscaping.net) to DA 94 (Pinterest.com). Likewise, Page Authority (PA) also ranges from 30 to 97.
DA and PA are the combined strength of backlinks earned by the site/page respectively. While these are not the exact parameters that the search engines use to rank sites, they are powerful indicators you can use to know how authoritative a site is.
Finally, look for the social shares the pages have got.
c) Online Reputation:
Social shares and likes tell how popular the content is. There are two ways to find this.
First, visit the respective pages. Usually, most of the sites display social shares and likes like this:
Alternatively, you can use the Ubersuggest tool for this as well. Put the URL of the page into the tool and it’ll show all the social media shares, likes, pins, etc. like this:
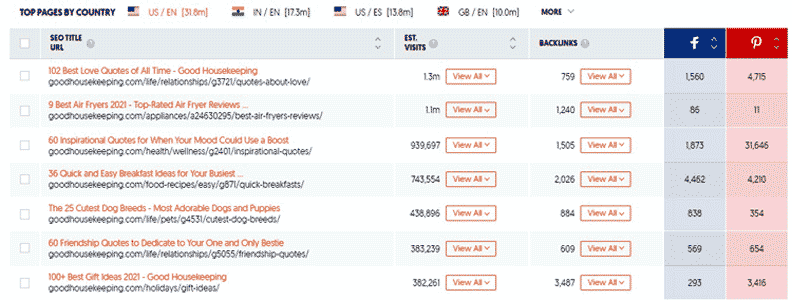
Look at the shares and pins — this tells how popular their content is.
So far we have conducted keyword research and competitive analysis, where we analyzed top search results, their backlink profiles, DA/PA, and social shares.
Well done!
We will use these findings in the next step –a very crucial one!
Method #2: Use an SEO Tool
Benchmarking your SEO performance is one thing, but intelligent marketers also look at their competitors’ performance and strategies to see where they’re succeeding and where they’re failing.
So, where to begin, and how should you evaluate your rivals?
Again, I’m using SEMrush for competitive research. You can use the tool of your choice.
• Make a list of all of your competitors. You’ll most likely be able to do this based on your company’s competitive study.
It’s still essential complementing this with a look at your SERP competitors (these are the businesses that have a substantial keyword overlap with yours).
These can be found in the Organic Research Tool’s ‘Competitors’ tab, where you’ll notice the most prevalent keywords with your domain.
• This tool’s ‘Pages’ tab will show you which pages get the most organic traffic. This knowledge can assist you in determining the type of content you should use to rank.
Pay close attention to whether traffic is mainly driven by blog content, product and category sites, or other sorts of content since this can help you find areas where you should focus your efforts.
• Utilize Keyword Gap Tools to see which keywords are ranked for by your competitors and which aren’t. It’s an activity worth doing now to see how your rivals are performing for specific keywords.
• Filling details of your domain and up to four competitors is all it takes to use this tool. From here, you’ll be able to see how each of your competitors stacks up against you in terms of the keywords you’ve selected. Make use of this information to help you plan out your keyword approach.
• Examine your competitors’ link profiles using the Backlink Analytics Tool to see how they build the links and where they come from. It’s also critical to use this information to estimate the magnitude of any link gaps between your domain and that of your competitors. This difference is commonly expressed in terms of the number of referring domains rather than total backlinks.
Step #3: Content Strategy
For optimum results, we have to analyze the search landscape across your niche/industry, identify the topics and relevant keywords to target.
Likewise, you will want to create content keeping the search intent in mind.
An SEO-focused content marketing approach will help you rank higher on Google. Also, you will be able to provide a better experience to your customer.
With this, on one hand, you will earn tons of relevant backlinks. On the other, you will also be able to satisfy your customers.
SEO Content Strategy includes:
1. Making a list of topics.
2. Prepare a list of primary and long-tail keywords based on these topics.
3. Create content clusters around selected keywords.
4. Plan your blogging schedule.
5. Rinse and repeat
1) Defining Your Pillar Pages & Topic Clusters
What is pillar content? Pillar content is a website page that serves as the content hub for a broader topic. It focuses on one of the main themes of your website.
What is a topic cluster? A topic cluster (also known as a content cluster) is a group of sub-topics that collectively cover a high-level topic (broad subject of the pillar content).
For instance, SEO strategy is a Pillar Content topic. And cluster topics may include on-page SEO, off-page SEO, link building, content writing, content marketing, technical SEO, etc.
Topic clusters are an excellent way to leverage the broad subjects through pillar pages. These provide an excellent internal linking opportunity and help search engines (as well as your users) find your content.
Pillar Pages and Primary Keywords
After establishing the objectives and KPIs, it’s time to go right into keyword research and, in particular, define the site’s significant keywords, which you’ll use for targeting with the pillar pages.
But before we go on to keyword research, let’s take a closer look at the concept of pillar pages. If you are new to the term, a pillar page is a page that acts as the foundation for a topic cluster.
In a nutshell, topic clusters let you concentrate on controlling the SERPs for certain themes. This approach is proven to generate tight topic relevancy for your site areas that differ from focusing on particular keywords.
Therefore, it’s better to map out your topic clusters early in developing your strategy so you can create a content strategy around them.
While you may be used to conducting keyword research, if you start from scratch with a topic cluster strategy, you must start with determining the objective for the pillar pages.
Rather than the precise long-tail keywords or subtopics, these keywords identify topics at a general level.
So to begin, identify the themes around which you’ll develop clusters. Make sure whether a topic has enough depth to support a cluster.
Defining the Cluster Content & Finding Long-tail Keywords
As you build out your topic cluster, click on those you think are relevant to see more ideas about subtopics and other areas of consideration.
Keep in mind that you must confirm the keywords before you make use of the Keyword Overview Tool for the pillar page. At that instance, you mainly try establishing the primary keyword goals for different pillar pages.
After finishing this step, your site should contain a list of topic clusters.
Consider the information that delves into a particular aspect of a topic in detail. This could include question and answers, how-to tutorials, or even opinion articles on current events.
First, however, how do you determine which keywords to aim for cluster subject matter?
Start by learning what long-tail keywords are if you are not well-versed with the concept:
Long-tail keywords are terms that are less commonly searched than more popular terms, typically because they are more precise.
The majority of long-tail keywords are usually three or more words in length. However, the size of a keyword does not determine whether it is long-tail or not. The term “long-tail keyword” comes from Google’s search results graph.
Consider the objective and depth of these pages to see which ones could be used as a cluster page. Long-tail keywords can be found easily by asking questions, and you can limit the Keyword Magic Tool to reveal these.
You want to plan out the supporting content that fits surrounding your pillar page. Ensure that there’s no overlap between two or more pages and that each piece of cluster content is aimed at a specific focal region.
Building the Topic Clusters
It’s time to start creating content out once you’ve selected your pillar pages and cluster content within a topic cluster.
You must understand what a searcher expects to see when they conduct a query search. This aids in the creation of content that engages users and leads to conversions.
For instance, if somebody searches for ‘shoes,’ they haven’t mentioned the kind, color, or even design of shoes they want. From this query, you could expect to land on a website with the possibility to browse different types of shoe styles.
However, if a user searched for ‘Adidas Sneakers,’ you’d look to encounter these things on a subcategory page. Therefore, a crucial thing to consider when creating subject clusters is understanding the search intent.
2) SEO Content Creation & Optimization
1) Take Advantage of Google Itself
How?
By analyzing Google’s first page.
As we already performed competitive research above, we know what is already ranking.
What type of content Google is showing on its first page?
Take a look at the top results. Visit those pages. Analyze how long the content is (word count), how the content is presented (design, images, etc.), etc.?
Now we have an idea of what is working for a particular keyword or a topic.
Then,
2) Create Something Better Than the Existing Ones
Yes, create epic content around that keyword or a topic. Create super high-quality content that is far better in terms of research data/facts/features, length, presentation/design, etc.
For example, if the top result has a list of 15 best trees for your backyard, you will want to create something like “25 or 30 best trees for your backyard”. Also, add more content around each topic/sub-topic. Likewise, include better, high-resolution images. You can even add infographics or videos for the same.
Let’s take another example: I was planning to write an article on Indian bloggers. When I searched on Google, I found that most of the content available has a list of 10-20 bloggers. So, I decided to list 40 plus Indian bloggers.

3) Stick To the Content Formats That Work
As it appears, certain content formats work best for SEO.
How?
There is no secret that search engines including Google use backlinks as a key ranking factor. In fact, backlinks are one of the top THREE ranking factors. The other TWO are Content and the RankBrain.
That means you need high-quality backlinks and lots of them.
Certain content formats such as “Why Post”, “What Posts”, “Infographics”, “List Posts”, and “How-To-Guides”, Original Research Data, etc. attract the most backlinks.
There, if you want to rank high on SERP in 2023, stick to content formats that have been proven to generate the most backlinks and shares.
Pro tip: By analyzing Google’s first page results, you know what formats are working for a particular search term.
4) Optimize Your Content for Search Intent
Search intent (or user intent) means the purpose behind an online search. It’s the “why” or “what” behind a search query.
What is the purpose? What they are looking for? Why did the person make this search? Want to learn something? Or want to buy something? Or something else?
Along the buyer’s journey, search intent is of crucial importance. However, the truth is that many SEO and content writers do not pay much attention to this.
As you are reading this guide, you have a good chance of getting an edge over your competitors — by optimizing your content for search intent.
First, optimize your content around the relevant keywords.
Next, format/render the content the way the user wants.
Pro tip: Again, analyze Google’s first page results. And design your content in the same format (with better/more depth).
5) Add Visual Appeal to Your Content
In 2023, long-form, image-heavy content will rank. Therefore, you need to prepare for the same.
Look at this content:

You see, even if the page is loaded with tons of information, it’s not going to get the desired traction.
Such essay-style formats do not work online.
Studies show web users do not “read”, they “scan”. (source)
Therefore, you need to present your content in a way that is easy to digest.
Make it scannable.
And, it’s relatively easy.
Here’re some incredibly simple ways to make your content more engaging:
i) Make shorter paragraphs. 2-4 sentences per para.
ii) Use headings and subheadings to break up longer passages.
iii) Use lots of scenes. The most effective visuals you can incorporate into your content are:
• Blog Post Banners
• Screenshots and Pictures
• Graphs and Charts
• Graphics and Visualizations
• Etc.
Step #4: On-page SEO
On-page SEO is all about optimizing the web page content for search engines (as well as users).
How to optimize your web pages?
For optimum results, you need to map out your entire on-page optimization process. These include content optimization, image optimization, interlinking, and more. Let’s discuss them in detail.
1) Optimize Page Content for SEO
Content optimization is the first step you should take for on-page SEO.
Optimize your page content for the target keywords. It’s always a good practice to include your target keyword in the beginning (in the first 100 words).
Also, include your keywords a few times in the body and at the end of the content.
The key point here is to use the primary as well as secondary long-tail keywords (Semantic SEO) strategically. It should be relevant and natural. By using your target keyword a few times, you tell Google what the page is about. But don’t stuff your content with a keyword. Keyword stuffing won’t work.
2) Optimize Page Titles (H1 Tag)
Next, include your keyword in Blog Post Title (H1 Tag). This is super important. Also, try to put the keyword at the beginning (or closer to the beginning). Every experienced SEO knows, it works.
Tip: Don’t make it longer than 50-60 characters.
3) Optimize Description Tags
In SEO, the Meta description tag is a summary of the page that Google displays (along with the URL and Post title) in a search engine results page (SERP).

Description Tags help Google (and users) to understand what the page is about. Optimizing your Description Tags for the target keywords is a great way to tell Google the same.
Similar to title tags, it’s easy to optimize your description Tags. Just create a unique summary for your page and include the primary keyword near the beginning.
Tip: Keep it between 150 and 160 characters. Else Google will truncate it in the results.
4) Optimize Subheadings (H2 Tags)
As we learned above, web users don’t read content word by word. Instead, they scan the page. Therefore, it’s better to chunk your content making it easy to skim. For this, one of the best methods is to use a lot of H2 subheadings.
Here, you can utilize this opportunity for on-page SEO – by optimizing H2 tags for your primary and/or secondary keywords.
Pro tip: Add the current year to your Title and Description Tags like this:
5) Optimize URLs for SEO
For better SEO traction, short, keyword-Rich URLs work best.
First, make your URLs short. Studies show that Google prefers shorter page addresses.
Second, include your target keyword in your URL.
For instance, the URL of one of the blog posts is start-a-blog, where “Start a Blog” is the primary keyword.
Tip: Either you use the “target keyword only” or the “target keyword plus one more word”.
6) Optimize Images (ALT Attribute)
As we discussed above, images and other types of visuals are a great way to make your content engaging and scannable.
When you use images, make sure to optimize them as well, by using keyword-rich anchor texts.
First, give your image a descriptive filename.
Second, optimize them with keyword-rich alt text.
This helps Google understand what each image is showing.
For example, for this article, I’ll optimize my image name as seo-strategy-tips.jpg and will use that same keyword (SEO strategy) as part of your image alt attribute.
Pro tip: Whenever possible, use original graphics. This will make your content stand out from your competition. Which will help you to get more likes, shares, and possibly some backlinks.
7) Internal Linking
Internal linking is one of the best (and the easiest) on-page SEO practices.
It’s HUGE.
How to interlink?
Link from higher-authority pages on your site to new or lower-authority pages that need to be promoted.
For better SEO performance, you should be actively interlinking your pages.
8) On-page SEO (Bonus Tips)
In addition to the tips discussed above, below are more tips that you will want to incorporate into your on-page SEO strategy. These include:
Boost Your Page Speed:
Page speed is one of the important SEO factors. Better page speed is also crucial for user engagement. You can speed up your site by:
• Reducing your page’s total size
• Remove render-blocking JavaScript
• Leverage browser caching
• Optimizing images
• Reducing the third-party scripts
• Minifying CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
• Reducing the number of redirects
• Improve server response time
• Use a content distribution network (CDN)
• Getting a better hosting service provider
Write Long-form Content:
Google likes long-form content. Step-by-step tutorials and original research data get most of the shares, likes, and backlinks. This, in turn, will take you to the top of Google search results.
So, create in-depth, actionable guides and articles that are easy for your users to follow.
Link to External Resources:
Don’t forget to link to external resources where deemed necessary. External linking helps you in two ways:
#1: It helps Google figure out your page topic.
#2: Google sees that your page as a trusted source of information (an authority). (Think, Google E-A-T)
There’s a thin line separating great content with the on-page SEO, but there’s no denying that you must ensure that these pieces are optimized as per your keyword strategy.
In a nutshell, on-page SEO entails optimizing the following:
• Title tags
• Meta descriptions
• H1, H2, H3 tags
• Internal linking, etc.
Although on-page SEO may appear to be SEO basics, improving these factors is a proven approach for improving your page’s organic visibility.
For this, you can use an SEO tool such as Semrush On-Page SEO Checker, etc. While it’s not mandatory at all, with an effective tool you may get some best recommendations in minutes. It will also tell why you must consider implementing these. That will help you enhance your on-page optimization.
After on-page SEO, it’s time to focus on off-page SEO or link building.
Step #5: Mastering the Off-page SEO
So far, we did keyword research, competitive research, content planning, and content writing and optimization.
The next step is to promote the blog. This includes Off-page SEO, social media marketing, content marketing, and paid ads.
In this section, we will concentrate on off-site SEO and link building.
To improve the SEO of your website, whatever actions you take outside of your site is called off-page SEO.
Build and they will come approach doesn’t work in SEO. Even the most amazing content won’t rank high on Google if it has no backlinks.
Backlinks are still one of Google’s three top-ranking factors. Without a robust link-building plan, you will struggle to rank high for competitive search queries.
This means that if you want to spur growth and reach your objectives, you’ll need to devise a strategy that aids in acquiring high-quality backlinks.
Backlinks are like votes from others on the web. The higher the number of quality backlinks, the better the Google search rankings.
When you earn and/or build a lot of authority backlinks, Google and other search engines see you as a trusted source of information. It’ll help you get to the top of search engine result pages (SERP).
The point to note here is, all backlinks aren’t created equal. Relevance and the page authority (PA) of the linking domain are paramount.
For example, if your site is about health and fitness, a backlink from a political article does not make sense. Google will see this as spam which is not good for your SEO.
Likewise, a link from a low PA page has little or no impact.
You need contextual links from high-authority sites. A single link from a relevant DA 90 domain is more powerful than the 100 backlinks low authority sites.
While marketers use various SEO strategies to build backlinks, the following are some of the most effective link building techniques:
• Link earning with content marketing
• Resource page link building
• Broken link building
• The Skyscraper Technique
• Creating linkbait and promoting it
• Guest blogging
• Digital PR
• Steal your competitors’ backlinks

Step #6: Technical SEO
Technical SEO is all about finding and fixing the technical issues concerning SEO. It focuses on your website’s backend architecture. The most important elements of technical SEO include website architecture, rendering, security, site speed, and crawling and indexing issues.
Steps you can take to improve the technical SEO of your website:
• Apply SSL – Migrate your site to HTTPS protocol
• Improve site load time for both, desktop and mobile
• Fix broken internal and outbound links and redirect issues; eliminate 404’s or broken pages
• Get rid of any mixed, duplicate, or thin content issues
• Make sure your URLs have a short and clean structure
• Disavow toxic backlinks
• Create an optimized XML sitemap and submit it to search engines
• Make sure your site has an optimized robots.txt file
• Update your site for Google’s new page experience signals and Core Web Vitals
• Check for crawl errors and solve them, if any
• Add structured data or schema markup for optimum performance
Google cares just as much about technical SEO as it does for content.
If your site has some technical concerns regarding SEO, they may stifle its efficiency and prevent it from ranking as effectively as it might if these issues were addressed.
Using an SEO tool like the Semrush Site Audit Tool, you may identify technical SEO flaws and gain insight into the faults or flaws that may be holding your site behind.
Step #7: Monitoring and Evaluation
1) Analyzing and Refining SEO Performance
After you’ve developed your SEO strategy and started putting it into action, you should revisit it regularly to evaluate and enhance it.
Analyzing and refining your SEO performance should be an important part of your SEO strategy. There’s no such thing as a ‘completed’ SEO campaign, and there’s always room for improvement.
Therefore, you must continually evaluate and refine your work to ensure that it is successful, whether you’re developing new content, optimizing or improving what you’ve previously generated, or ensuring that no technical issues arise.
Remember how you set targets and KPIs early in the process of developing your strategy? You should measure and report on them periodically (ideally at least once a month) to ensure that your performance is on track to accomplish your objectives. Adopt a growth mindset and concentrate your efforts on reaching success.
2) Auditing the Existing Content
Likewise, you should improve and update your content. Also, you should measure and track your content’s success.
It’s amazing to assess your existing content before you start building up and creating new material to see if any existing pieces might be enhanced or fit into the current topic clusters.
You can use the Semrush Content Audit Tool to assist you with this. A content audit primarily assists you in identifying content that you should either:
• Keep
• Update
• Delete
Begin with what you already have before developing anything new is the goal of auditing the content. Mostly, according to the available data, you will be able to make your present content work better.
Taking time for auditing the site’s content lets you make data-driven decisions, concentrate your energy on achieving your objectives, and identify that upgrading existing material yields better results than developing new content.
Final Words on SEO Strategy
There you have it: The actionable guide for creating a profitable SEO strategy in 2023.
The SEO process mostly targets content strategy & optimization, content marketing, organic link building, and search engine result placement.
However, you can also implement your SEO strategy along with more aggressive measures such as paid advertising or traditional marketing campaigns.
You’re working blindly if you don’t have an SEO strategy in place. Take time to develop your SEO strategy that explains the website’s long-term goals and helps out everyone on your team.
Establishing an applicable SEO strategy is all about defining what you’re going to do about various stakeholders in a way that makes sense and offers everybody involved a clear focus.
When it comes to putting together a good SEO plan, having a method to follow might be beneficial. As you’ll need to customize this for your own company, it’s an excellent place to start so you’re on the right course and considering the correct target areas.
And, don’t forget to work on your plan.
JD Bhatala is a Content Marketing Strategist with over 15 years of experience. He is the co-founder of Web Content Edge where he helps online businesses gain visibility and increase traffic, leads, and sales. Catch him online at Twitter or LinkedIn.

